

간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌입니다.
다음 문서를 기반으로 작성했습니다.
https://www.sheshbabu.com/posts/rust-module-system/
2022. 9. 12 최초작성
2022. 4. 17 최종작성
Rust 개발 환경 만드는 방법은 아래 포스트를 참고하세요.
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2110
Rust에서는 use 경로에 사용할 수 있는 다음 키워드를 사용하여 원하는 module을 빠르게 가져다 사용할 수 있습니다:
crate - root module
super - 현재 module의 부모 module
self - 현재 module
예제 1
main 모듈(main.rs)에서 config 모듈(config.rs)을 가져오는 예제입니다.
main 모듈(main.rs)에서 불러와 사용할 config 모듈을 main.rs 파일과 같은 디렉토리에 config.rs로 두거나

main.rs 파일이 있는 경로에 config 하위 디렉토리 내의 mod.rs 파일로 둘 수 있습니다.

main.rs
| // config 모듈을 로드하기 위해 config.rs 또는 config/mod.rs를 찾습니다. mod config; fn main() { // ::를 사용하여 config 모듈의 print_config 함수를 호출합니다. config::print_config(); println!("main"); } |
config.rs
| // 디폴트가 비공개이므로 pub 키워드를 사용해야 합니다. pub fn print_config() { println!("config"); } |
예제 2
route/health_route.rs에 정의된 print_health_route 함수를 main.rs에서 호출하는 예제입니다.
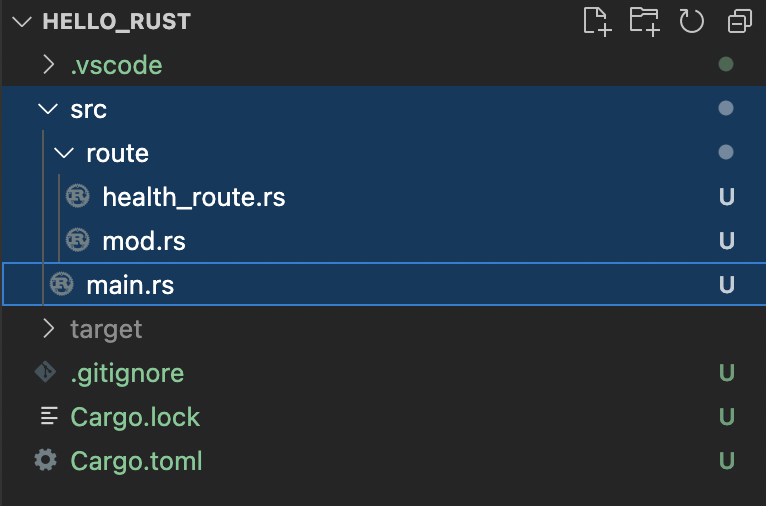
mod 키워드는 같은 디렉토리에 있는 route.rs 또는 route/mod.rs에만 사용할 수 있습니다.
따라서 main.rs에서 route/health_route.rs 내부의 함수를 호출하려면 다음 작업을 수행해야 합니다.
1. route/mod.rs라는 파일을 만들고 main.rs에서 route 모듈을 mod를 사용하여 가져오도록 합니다.
2. route/mod.rs에서 health_route 모듈을 mod를 사용하여 가져오도록 합니다. 이때 mod 앞에 pub 키워드를 추가해야 합니다.
3. health_route.rs에서 print_health_route 함수를 정의시 pub 키워드를 추가해야 합니다.
main.rs
| mod route; fn main() { // route/health_route.rs에 있는 print_health_route 함수를 호출합니다. route::health_route::print_health_route(); println!("main"); } |
route/mod.rs
| pub mod health_route; |
routes/health_route.rs
| pub fn print_health_route() { println!("health_route"); } |
실행 결과

예제 3
main 모듈이 아닌 모듈에서 다른 모듈의 함수를 호출해봅니다.
main.rs에서 routes/user_route.rs의 print_user_route를 호출하고 routes/user_route.rs의 print_user_route에서 models/user_model.rs의 print_user_model을 호출하는 예제입니다.
코드 구성을 다음 스크린샷처럼 합니다.

각각의 코드입니다.
main.rs
| mod route; mod models; fn main() { // route/user_route.rs에 있는 print_user_route 함수를 호출합니다. route::user_route::print_user_route(); println!("main"); } |
route/mod.rs
| pub mod user_route; |
route/user_route.rs
| pub fn print_user_route() { // main이 아닌 모듈에서 다른 모듈을 호출합니다. // crate는 root 모듈을 의미합니다. // root/models/user_model.rs에 있는 print_user_model 함수를 호출합니다. crate::models::user_model::print_user_model(); println!("user_route"); } |
models/mod.rs
| pub mod user_model; |
models/user_model.rs
| pub fn print_user_model() { println!("user_model"); } |
super
파일 구성이 여러 디렉토리에 있는 경우 이름이 너무 길어집니다. print_user_route, print_health_route를 호출한다면 각각 crate::route::health_route와 crate::route::user_route 경로를 사용해야 합니다.
crate::routes::health_route::print_health_route()를 사용하여 함수를 호출하는 대신 super::health_route::print_health_route()를 사용하여 호출할 수 있습니다. 상위 경로를 참조하기 위해 crate::routes 대신에 super를 사용하는 것입니다. super는 현재 모듈의 부모 모듈을 의미합니다.

main.rs
| mod route; fn main() { println!("main"); // route/user_route.rs의 print_user_route 함수를 호출합니다. route::user_route::print_user_route(); } |
route/mod.rs
| pub mod user_route; pub mod health_route; |
route/user_route.rs
| pub fn print_user_route() { println!("user_route"); // crate/route/health_route.rs 파일에 있는 print_health_route 함수를 호출합니다. // crate::route::health_route::print_health_route(); // crate::route를 super로 줄여서 적을 수 있습니다. super::health_route::print_health_route(); } |
route/health_route.rs
| pub fn print_health_route() { println!("health_route"); } |
실행 결과
main.rs에서 main을 출력하고 route/user_root.rs의 print_user_route 함수를 호출합니다.
route/user_root.rs의 print_user_route 함수에서 user_root를 출력하고 route/health_route.rs의 print_health_route 함수를 호출합니다.
route/health_route.rs의 print_health_route 함수에서 health_route를 출력합니다.
main
user_route
health_route
use
앞에서 사용한 route/user_route.rs 파일에 use 키워드를 사용하면 긴 모듈 경로를 줄일 수 있습니다.
원래는 다음처럼 긴 경로를 사용하여 함수를 호출해야 합니다. (앞에서 살펴본 super를 사용하여 create::route를 대체할 수도 있었습니다.)
| pub fn print_user_route() { println!("user_route"); crate::route::health_route::print_health_route(); } |
use를 사용함으로써 함수를 호출하는 부분의 코드가 다음처럼 짧아집니다.
| use crate::route::health_route::print_health_route; pub fn print_user_route() { // crate::route::health_route::print_health_route(); print_health_route(); println!("user_route"); } |
추가로 as 키워드를 사용하면 print_health_route 함수 이름 대신에 원하는 다른 이름인 log_health_route 함수 이름을 사용하도록 할 수 있습니다.
| use crate::route::health_route::print_health_route as log_health_route; pub fn print_user_route() { // crate::route::health_route::print_health_route(); log_health_route(); println!("user_route"); } |
외부 모듈
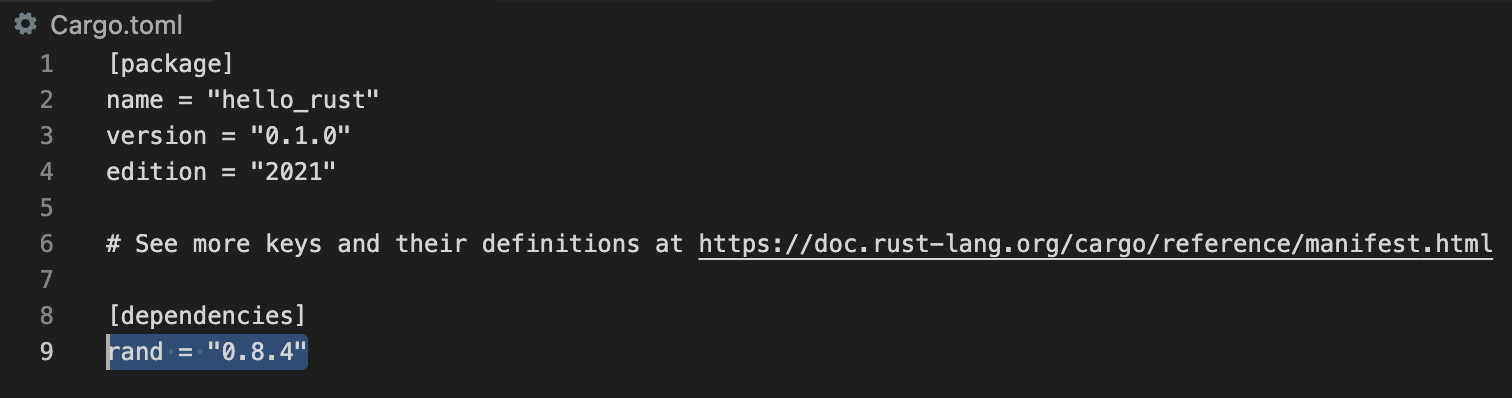
Cargo.toml 파일에 사용할 모듈을 추가하면 프로젝트 내부의 모든 모듈에서 추가된 모듈을 전역적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
rand 모듈을 사용하기 위해 Cargo.toml 파일의 dependencies 항목에 rand = “0.8.4” 라고 추가합니다.
좀 더 쉬운 방법으로 사용할 모듈을 추가하는 방법은 아래 포스트를 참고하세요.
Rust의 Cargo.toml에 의존성 패키지 추가/삭제하는 방법
이제 다음 두가지 방식으로 rand 모듈의 random 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다.
| fn main() { let random_number: u8 = rand::random(); println!("{}", random_number); } |
| use rand::random; fn main() { let random_number: u8 = random(); println!("{}", random_number); } |
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 1 : 변수, 상수, 함수, 튜플, 배열, 데이터타입, println
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2194
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 2 : if-else, loop, while, for, match, struct, method
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2195
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 3 : 열거형, 제네릭 데이터 타입, Option, Result, unwrap, vector
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2196
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 4 : 소유권, 참조, 역참조, 생명주기
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2197
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 5 : 문자열, utf-8
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2198
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 6 : 모듈
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2199
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 7 : &self, &mut self, trait, 동적 디스패치, 정적 디스패치, Generic 메서드, Box
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2200
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 8 : 참조자, 댕글링 참조, 원시 포인터
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2203
간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 9 : Box, 재귀적 데이터타입, Deref 트레잇
https://webnautes.tistory.com/2202
'Rust > Rust 강좌' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 9 : Box, 재귀적 데이터타입, Deref 트레잇 (0) | 2023.10.28 |
|---|---|
| 간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 7 : &self, &mut self, trait, 동적 디스패치, 정적 디스패치, Generic 메서드, Box (0) | 2023.10.28 |
| 간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 5 : 문자열, utf-8 (0) | 2023.10.28 |
| 간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 4 : 소유권, 참조, 역참조, 생명주기 (0) | 2023.10.28 |
| 간단하게 정리해본 Rust 강좌 3 : 열거형, 제네릭 데이터 타입, Option, Result, unwrap, vector (0) | 2023.10.28 |
시간날때마다 틈틈이 이것저것 해보며 블로그에 글을 남깁니다.
블로그의 문서는 종종 최신 버전으로 업데이트됩니다.
여유 시간이 날때 진행하는 거라 언제 진행될지는 알 수 없습니다.
영화,책, 생각등을 올리는 블로그도 운영하고 있습니다.
https://freewriting2024.tistory.com
제가 쓴 책도 한번 검토해보세요 ^^

그렇게 천천히 걸으면서도 그렇게 빨리 앞으로 나갈 수 있다는 건.
포스팅이 좋았다면 "좋아요❤️" 또는 "구독👍🏻" 해주세요!





